Difference between revisions of "SOCR Events OHBM2013 Workflows"
(→Agenda) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Agenda== | ==Agenda== | ||
* 8:00-8:10 Introduction | * 8:00-8:10 Introduction | ||
| − | * 8:10-8:35 The Pipeline Workflow Environment, Ivo Dinov, Pipeline Team, UCLA | + | * 8:10-8:35 The [http://socr.ucla.edu/docs/slides/OHBM_Workflows_Dinov_Intro_PipelineSlides.pptx Pipeline Workflow Environment (PPTX)], Ivo Dinov, Pipeline Team, UCLA |
* 8:40-9:05 [http://www.bmi.emory.edu/davidgutman PTSD/TBI Morphometrics using the Pipeline], David Gutman, Emory | * 8:40-9:05 [http://www.bmi.emory.edu/davidgutman PTSD/TBI Morphometrics using the Pipeline], David Gutman, Emory | ||
* 9:10-9:35 [http://nipy.sourceforge.net/nipype Neuroimaging in Python (NiPy) Architecture], Jarrod Millman, Berkeley | * 9:10-9:35 [http://nipy.sourceforge.net/nipype Neuroimaging in Python (NiPy) Architecture], Jarrod Millman, Berkeley | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 13 June 2013
Contents
[hide]SOCR News & Events: OHBM 2013 Workflows Education Course
Event Logistics
- Organizer: Ivo Dinov
- Event: OHBM 2013 Conference
- Education Course Title: Neuroimaging ‘Big Data’ Challenges and Computational Workflow Solutions
- Place: Seattle, Washington USA
- Venue: Washington State Convention Center, 800 Convention Place, Seattle, WA 98101-2350, Phone: 206-694-5000, Fax: 206-694-5399, Email: info@wscc.com, Room 607 (level 6)
- Date: Sunday, June 16, 2013.
- Time: 8:00AM – 12:00PM Pacific Time
- Registration: All speakers, presenters and attendees must register and pay the meeting registration fee.
- URL: http://ucla.in/1971hZM
Agenda
- 8:00-8:10 Introduction
- 8:10-8:35 The Pipeline Workflow Environment (PPTX), Ivo Dinov, Pipeline Team, UCLA
- 8:40-9:05 PTSD/TBI Morphometrics using the Pipeline, David Gutman, Emory
- 9:10-9:35 Neuroimaging in Python (NiPy) Architecture, Jarrod Millman, Berkeley
- 9:40-10:05 Single subject fMRI Workflow, Satrajit Ghosh, MIT
- 10:10-10:25 Coffee Break
- 10:30-10:55 Pipeline system for Octave and Matlab (PSOM), Pierre Bellec, l'institut de gériatrie de Montréal and Université de Montréal
- 11:00-11:25 Configurable PSOM Pipeline for the Analysis of Connectomes (C-PAC), Cameron Craddock, Virginia Tech
- 11:30-11:55 The Swift parallel scripting language and computational neuroscience applications, Michael Wilde, UChicago
- 11:55-12:00 Conclusion/Evaluations
- Interactive Web-based Q&A Forum for this Workshop Enter Code *769983* followed by a space and the comment, questions, text of message (part of the larger OHBM'123 online book)
Course Description
There are Peta bytes of neuroimaging data, 10,000’s of computational algorithms reported in the literature, 1,000’s of independently developed software tools, and 100’s of protocols for analyzing structural, functional, diffusion and spectroscopic neuroimaging data. The demand for sophisticated data management skills, choice of appropriate software tools and reliable computational protocol, and the broad gamut of possible result interpretations require significant multidisciplinary expertise and robust computational infrastructure. Rather than presenting a forum for discussing the theoretical and methodological aspects of neuroimaging and brain mapping, the focus of this education workshop will be on training, practical usage, functionality and applications illustrating tool utilization, software scope and limitations, and available computational infrastructure.
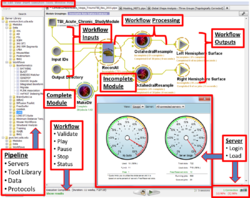
This course will include paired training and application demonstrations on using different graphical and script-based pipeline workflow architectures to manage, process, analyze and visualize large volumes of neuroimaging and genetics data. Attendees will learn to use several concrete end-to-end pipeline workflow solutions for imaging (sMRI, fMRI, DTI) and phenotypic (demographic, genetic, clinical) data in development, aging and pathology. Examples of workflow solutions that will be demonstrated include the LONI Pipeline, Neuroimaging in Python (NiPy), Pipeline system for Octave and Matlab (PSOM) and SWIFT.
Learning Objectives
- Understanding of the benefits of employing a pipeline workflow infrastructure for large-scale Neuroinformatics, and identification of differences between alternative workflow architectures.
- Ability to find, modify, execute, monitor and interpret the results of common computational pipeline protocols.
- Working knowledge of validating, sharing and reviewing computational neuroimage processing protocols as pipeline workflows.
Target Audience
Three types of learners would benefit from this training workshop – experienced investigators (interested in sharing their computational protocol with wider audiences), novice users (looking for high-throughput data processing capabilities), neuroimaging system administrators (searching for distributed, computationally efficient and efficient mechanism to support heterogeneous image computing cluster systems).
Translate this page: