Difference between revisions of "SMHS Epidemiology"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | * SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.umich.edu | ||
==[[SMHS| Scientific Methods for Health Sciences]] - Epidemiology == | ==[[SMHS| Scientific Methods for Health Sciences]] - Epidemiology == | ||
| Line 330: | Line 332: | ||
*Model 4: The genotype and the risk factor each influence risk by themselves: | *Model 4: The genotype and the risk factor each influence risk by themselves: | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | [[Image:SMHS Epi Figure 13.png| 500 px]] | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | *The study of gene-environment interactions, use epidemiologic techniques to identify both components (gene and environment): | ||
| + | **Case-control studies | ||
| + | **Cohort studies | ||
| + | **Case only studies | ||
| + | **Case-parental control | ||
| + | **Affected relative pair | ||
| + | **Twin studies | ||
| − | + | To model Gene-Environment interactions:$ outcome = gene + environment + gene-environment interaction. Y=G+E+GXE $ | |
Revision as of 13:33, 22 August 2014
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.umich.edu
Contents
Scientific Methods for Health Sciences - Epidemiology
Overview:
After a general introduction to the filed of Epidemiology, students can have a basic idea of the language of Epidemiology. In this course, we want to identify and describe the population patterns of health-related risk factors and health-related outcomes in terms of persons, place and time. We are interested in exploring current major public health issues and try to identify and evaluate the main determinants of such public health issues (e.g. demographic, genetic, infectious, behavioral, and social). With all the concepts and methodologies of analysis in Epidemiology, application would be the next step. Here we examine and apply analytical approaches to data from different epidemiologic study designs (e.g., cross-sectional, cohort, randomized studies) and to critically appraise epidemiological findings.
Motivation:
Goals of this course:
- To understand basic features of the human genome and the distribution of mutations among individuals.
- To understand the principles of segregation and linkage as they apply to human pedigree analysis and the identification of genetic variations associated with disease.
- To learn population and quantitative genetic concepts that are necessary in order to study the relationship between genetic variation and disease variation in populations.
- To learn about prototypical gene-disease relationships that are important to public health.
- To understand the key issues in genetic testing in populations.
- To understand the genetic complexity of common chronic disease.
- To have a basic understanding of the importance and biological basis of epigenetic mechanisms, gene-environment interactions, and gene-gene interactions.
Theory
- Public Heath Genetics:some current and potential applications of genome research include:
- Molecular medicine: improved diagnosis of disease; earlier detection of genetic predispositions to disease; rational drug design; gene therapy and control systems for drugs; pharmacogenomics “custom drugs”.
- Microbial genomics: new energy sources (biofuels); environmental monitoring to detect pollutants; protection from biological and chemical warfare; safe, efficient toxic waste cleanup.
- Risk assessment: assess health damage and risks caused by radiation exposure, include low-dose exposures; assess health damage and risks caused by exposure to mutagenic chemicals and cancer causing toxins.
- Bio-archaeology, anthropology, evolution, and human migration: study evolution through germline mutations in lineages; study migration of different population groups based on X chromosome or Y chromosome; compare breakpoints in the evolution of mutations with ages of populations and historical events.
- DNA forensics (identification): identify potential suspects whose DNA may match evidence left at crime scenes; exonerate persons wrongly accused of crimes; identify crime and catastrophe victims; establish paternity and other family relationships; determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds.
- Agriculture, livestock breeding, and bioprocessing: more nutritious produce; Biopesticides; healthier, more productive, disease-resistant farm animals; new environmental cleanup uses for plants like tobacco.
- The Human Genome and Mutation
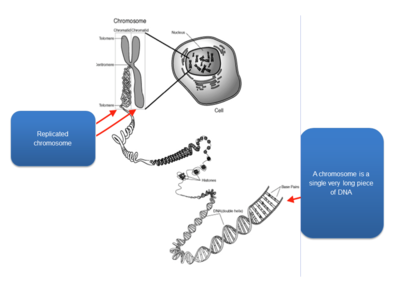
- Chromosomes are highly condensed DNA:
- Chromosomal banding pattern: condensed chromosomes can be stained to create the appearance of dark and light bands; dark bands represent regions rich in As and Ts; each band contains millions of DNA nucleotides; each chromosome has a unique banding pattern.
- A human karyotype: depicts the entire chromosomal constitutions of a person; normal karyotypes have 46 chromosomes; we get 23 chromosomes from each parent (22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome).
- Chromatin: composed of DNA and proteins that are associated with the chromosomes. (1) Euchromatin: lightly condensed DNA; gene rich, often actively transcribed. (2) Heterochromatin: highly condensed DNA; often composed of repetitive DNA elements; centromeres and telomeres.
- Centromeres: large arrays of repeated DNA sequences; spindle fibers attach during mitosis to separate sister chromatids.
- Telomeres: arrays of repeated DNA sequences that are often thousands of bases in length; a “cap” at the end of chromosome to provide stability; due to the way that chromosomes replicated, telomeres, shorten with each cell division in human somatic cells.
- International system for human cytogenetic nomenclature: short arms of a chromosome are labeled; long arms are labeled; chromosome bands are labeled p11, p12, etc. like a zip code; the terminal ends of the chromosomes are labeled ter; where the arms meet in the middle is the centromere.
- Genes are located on chromosomes: there are 45 bands on chromosome 5; chromosome 5 contains 1633 genes; chromosome 5 ~ 181000000 bases long; genes are referred to by their chromosomal location.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: there are two types of abnormalities that can occur on a chromosomal level in humans: (1) structural abnormalities – missing, extra, or rearranged genetic material on one particular chromosome; (2) numerical abnormalities – deviations in the total number of chromosomes that an individual has.
Changes in chromosome structure.
Deletion: 46, XY, del(6) (p16.3) Terminal deletion with breakpoint at 6p16.3
Duplication: 46, XX, dup(1) (q22q25) Duplication of chromosome 1 region q22 to q25
Insertion: 46, XY, ins(2;5) (p13;q21q31) An insertion of chromosome 5q21-31 into chromosome 2p13
Translocation: 46, XX, t(2;6) (q35;p21.3) A balanced reciprocal translocation with breakpoints in 2q35 and 6p21.3
Inversion: 46, XY, inv(11) (p11p15) An inversion on chromosome 11 with breakpoints at p11 and p15
- Mutations: caused by changes in the DNA sequence; there are many different types of mutations; can happen in somatic cells or during development of gametes.
Types of mutations: (1) Nucleotide substitutions, involve an alteration in the sequence but not the number of nucleotides (DNA bases) in a gene; (2) Insertions & Deletions, involve an alteration in the number of nucleotides in a gene; (3) trinucleotide repeats, involves an alteration in the number of times that a certain sequence of three bases repeats itself; (4) Splice Site Variation, involve an alteration in the non-coding region of a gene, which affects the way that parts of the gene sequence are combined to make RNA. Results of mutations: mutations in exons may result in – misspelling of protein (missense), truncation of the protein (nonsense), no effect; mutations in introns may result in – no effect, altered regulations of gene expression, splice site variation.
- Genes in Population:
- Gene pool: all available genetic variation in a population; all potential mating combinations.
- Basic concepts:
- Alleles: the type of genetic variation seen at a particular location on a chromosome. (1) fictional form: big “A” allele, little “a” allele; (2) base pair form: T allele at basepair 71349562 on chromosome 2, C allele at basepair 71349562 on chromosome 2; (3) codon form: Arginine at codon 124, Glycine at codon 124.
- Genotypes: we inherit one allele from our mother and one allele from our father to form our genotype. Variation in a single gene like AA, Aa or aa.
- Haplotypes: it is the combination of alleles that an individual has at multiple sites along a chromosome.
- Allele frequencies: the prevalence of a particular allele in a given population. Allele frequency = $\frac {Number\, of\, alleles\,}{2*(number\, of\, people\,)}$.
- Genotype frequencies: prevalence of a particular genotype in a given population.
- Haplotype frequencies: frequency that a haplotype occurs in different ethnic groups.
- Hardy-Weinberg disequilibrium: when genotype frequencies in a population differ from what would be predicted based on allele frequencies.
- Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE): in a stable population with random mating, allelic frequencies typically predict genotype frequencies using the law of independent segregation. When allele frequencies can accurately be used to predict genotype frequencies in a population, the population is considered to be in a HWE.
- HWE: suppose a SNP that can only be A or C $(p_{A}+p_{C}=1)$, and probability of having A allele is $p_{A}$, C allele is $p_{C}$, then under HWE, the probability of AA genotype = $p_{A}^{2}$, probability of having CC = $p_{C}^{2}$, the probability of having AC = $2p_{A}p_{C}$.
- Steps to test HWE: (1) estimate allele frequencies; (2) calculate the expected relative genotype frequencies under HWE; (3) calculate the expected number of people with each genotype; (4) calculate the difference between observed and expected number of people with each genotype using $χ^2$ formula; (5) sum up the $χ^2$ components and compare the sum to statistical tables to see if there is significant deviation.
| Observed | Expected | $X^{2}$ component | |
| AA | $N_{AA}$ | $p^{2}(N_{Total})$ | $\frac{(O_{AA}- E_{AA})^{2}}{E_{AA}}$ |
| Aa | $N_{AS}$ | $2pq^{2}(N_{Total})$ | $\frac{(O_{Aa}- E_{Aa})^{2}}{E_{Aa}}$ |
| aa | $N_{aa}$ | $q^{2}(N_{Total})$ | $\frac{(O_{aa}- E_{aa})^{2}}{E_{aa}}$ |
| $N_{Total}$ | $N_{Total}$ | Overall $X^{2}$ Statistics |
$N_{AA}$ is the actual number of people in the population with AA genotype, $N_{Total}$ is the number of people in the population, $p^{2}(N_{Total})$ calculated expected number of people with AA genotype. For $χ^{2}$, the null hypothesis $H_{0}$: the population is in HWE. For two alleles, if the overall $χ^{2}$ is less than or equal to 3.84, then p-value is greater than 0.05 and don’t reject $H_{0}$, population is in HWE; if $χ^{2}$ more than 3.84, p-value is less than 0.05, reject $H_{0}$, population is in HWD (disequilibrium).
- Pedigree Analysis and Probability in Genetics
- Mendel’s Law of Segregation: organism carry two copies of each genetic factor; there is segregation of parental factors during gamete formation; each gamete receives one genetic factor from each parent.
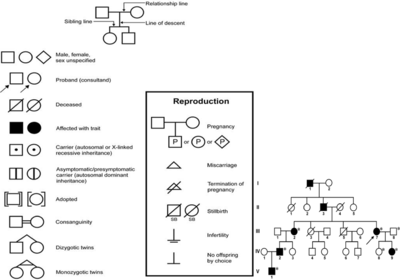
- Human Pedigree Nomenclature:
Modes of Inheritance:
- Autosomal dominant: individuals that inherit the dominant disease allele, D will develop the disease. Homozygous (DD: affected), Heterozygous (Dd: affected), Homozygous (dd: normal).
Traits: every affected individuals has an affected parent; there is 50% chance that each affect parent will transmit the trait to any child; the trait is expressed in both males and females is roughly equal numbers; two affected individuals may have unaffected children; the phenotype is often more severe in homozygous affected individuals.
- Autosomal recessive: individuals that inherit two copies of the recessive disease allele, d, will develop the disease. Homozygous (DD: normal), Heterozygous (Dd: normal), Homozygous (dd: affected).
Traits: for rare traits, most affected individuals are the children of unaffected parents; all of the children of two affected individuals are affected; the risk of an affected child from a mating a two heterozygotes is 25%; the trait is expressed in both males and females; for rare traits, the unaffected parents of an affected individual may be related to each other.
- Sex-linked dominant (X-lined dominant): $X^{C} X^{C}$ affected female, $X^{C}$ Y affected male, $X^{C} X^{c}$ affected female, $X^{c}$ Y normal male, $X^{c} X^{c}$ normal female.
- Sex-linked recessive (X-linked recessive): female that carry a recessive mutation $X^{C}$ will have affected male children. $X^{C} X^{C}$ normal female, $X^{C}$ Y normal male, $X^{C} X^{c}$ carrier female, $X^{c}$ Y affected male, $X^{c}X^{c}$ affected female.
Traits: there is no male to male transmission; there is mother to son transmission; female can be homozygous and have the trait. Examples may be color blindness.
- Probability in Pedigree Analysis: using Mendel’s Laws, we can estimate the probabilities of an offspring’s genotype if we know (or assume) a mode of inheritance; under Hardy-Weinberg, we can estimate genotype probabilities for parents.
- Steps: (1) choose a mode of inheritance; (2) establish the penetrance of each genotype under that mode of inheritance; (3) determine the potential genotypes of each person under that mode of inheritance; (4) determine the founder genotype probabilities (parent generation); (5) determine the transmission probabilities (offspring generation); (6) calculate the probabilities of each pedigree member given their phenotype, their genotype, and the penetrance of the disease P(member)=P(phenotype and genotype)=P(genotype)*P(phenotype|genotype); (7) calculate the total probability of the pedigree P(pedigree)$=∏_{i=1}^{n}$P(genotype)*P(phenotype|genotype), n is number of people in the pedigree.
In step 2, there can be complete penetrance or incomplete penetrance. With complete penetrance, individuals’ phenotype will always match their genotype. If a genotype has incomplete penetrance, some individuals with the ‘affected’ genotype will not exhibit the ‘affected’ phenotype. This happens often when the development of the phenotype is controlled by more than one gene or is modified by environmental factors.
- Founder effect: in small populations, rare recessive alleles present in a member of the original group of settlers is transmitted through successive generations; population expands and remains geographically and culturally isolated. After ~10 generations, children with recessive disease begin to appear, inbreeding is not usually a significant feature of the population.
Consanguineous mating: inbreeding (consanguinity) = mating between genetically related individuals; degree of inbreeding based on the probability that an individual will inherit two alleles that came from a common ancestor; homozygousity due to inheritance of alleles that are “Identical by Descent” (IBD).
Linkage Analysis
- Linkage concepts: genetic linkage refers to the study of the order of genes on chromosomes; distance between genes (aka genetic distance).
- Recombination fraction: a measure of distance between genes; alleles that are physically very close to one another on a chromosome tend not be separated by recombination as often as alleles that are physically far from one another. The symbol $\theta$ is used to show the probability that the alleles of two genes will recombine during gamete formation, it equals to the proportion of gametes that are recombinant = probability of recombination = recombination fraction.
- When two loci are inherited independently of each other, recombinants and non-recombinants are found in equal proportions in the offspring: $\theta$=0.5.
- When two loci are inherited together because of chromosome location, there are more non-recombinants than recombinants in the offspring: $0\le\theta\le0.5$.
- $\theta=0.5$ implies no linkage; $\theta=0$ implies complete linkage; $0<\theta<0.5$ implies linkage.
Parametric Linkage Analysis: requires to (1) collect pedigree data with many meiotic events (need multiple generations or many children); (2) make assumptions about how the disease is inherited (single locus vs. multilocus; dominant vs. recessive; penetrance; allele frequencies of disease susceptibility locus); (3) can be done with phase known (know how the alleles are distributed on parental chromosomes) or phase unknown (know which alleles come from which parent, but not how they are distributed on the chromosomes) pedigrees.
- For phase known pedigree: recombination fraction $\theta$=$\frac{\#\,recombinants}{\#\,informative\,meiosis'}$, where informative meiosis = parental gamete formation that provides information about recombination between two loci.
- For phase unknown pedigree: parent haplotypes are not known, $\theta$ cannot be estimated directly because there is no way to tell whether the offspring are recombinant or non-recombinant.
- Estimation of $\theta$ by the Maximum Likelihood Method: estimate $\theta$ for any pedigree by using MLE. This equation takes the data in the pedigree and asks the question, what $\theta$ would result in the largest L($\theta$) given the number of recombinant and non-recombinant gametes? L($\theta)=c(1-\theta)^{n-k}\theta^{k}$, where c is a constant, n is the number of informative meioses, k is the number of recombinant meioses, n-k is the number of non-recombinant
- lnL($\theta$)=lnc+(n-k) ln(1-$\theta$)+kln$\theta$, $\frac{∂lnL\theta}{∂\theta}=\frac {-n-k} {1-\theta}+\frac{k}{\theta}$=0,=$\hat {\theta}$ = $\frac{k}{n}$.
- Logarithm (base 10) Of Odds (LOD) score: The LOD score compares the likelihood of observing the test data if the two loci are indeed linked, to the likelihood of observing the same data purely by chance. LOD>0 indicate the presence of linkage, LOD<0 indicate that linkage is less likely.
In linkage analysis, the two hypotheses are $H_{0}$: no linkage, $\theta$=0.5; $H_{1}$linkage, $\theta=\hat{\theta}$.LOD score Z($\theta$)=$log_{10}\frac{L(\theta=\hat{\theta})}{L(\theta=\frac{1}{2})}$,where $L(\theta=\hat{\theta}$ is the likelihood equation when $\theta=\frac{1}{2}$.
| $\theta$ | LOD score |
| $\theta>0$ | $Z (\theta) = nlog(2) + k * log(\theta) + (N - k)log (1-\theta)$ |
| $\theta = 0$and k = 0 | $Z (\theta) = nlog(2)$ |
| $\theta = 0$ and k > 0 | $Z(\theta) =-\infty$ |
To test one hypothesis on multiple pedigrees, add the LOD scores of each individual pedigree to determine a final LOD score:
$Z(\theta)=\sum Z_{i}(\theta)$ for i=1,…,n pedigrees
$\theta$ is the value of $\theta$ that maximizes L($\theta$) = MLE.
LOD scores correspond to the following odds:
| $Z(\theta)=-2$ | 100:1 odds against linkage, significantly in favor of no linkages |
| $Z(\theta)=-1$ | 10:1 odds against linkage |
| $Z(\theta)=0$ | Not informative |
| $Z(\theta)=+1$ | 10:1 odds in favor of linkage |
| $Z(\theta)=+2$ | 100:1 odds in favor of linkage |
| $Z(\theta)=+3$ | 1000:1 odds in favor of linkage, significantly in favor of linkage |
-2 < LOD < 3 provides only weak (non-significant) evidence for or against linkage. LOD scores vary with $\theta$: calculate LOD scores for a range of $\theta's$, find one that maximizes Z($\theta$); vary with data: each pedigree gives different information; are additive across independent pedigrees: sum data from all pedigrees to get final Z score.
Example 1: Suppose the father and mother are both Dd (dd is the recessive affected individual, Dd the heterozygous carrier individual, and DD the homozygous normal individual). The table below shows the Mendelian ration of $\frac{3}{4}$ normal to $\frac{1}{4}$ affected. For most autosomal recessive diseases, the heterozygote cannot be distinguished from the normal homozygote. In the normal phenotype categories of offspring (Dd and DD produce the same normal phenotype), two of the three are heterozygotes (carriers); one of the three is homozygous normal
| Father | |
| Mother | 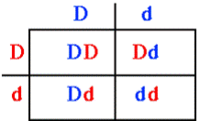
|
This pedigree example illustrates autosomal recessive inheritance. I-1 and I-2 are unrelated but produced an affected offspring (affected offspring have normal parents). By chance, they both must have been carriers. Even though II-2 is affected, she produced no affected offspring (i.e., the phenotype appears in siblings, not parents). As the probable genotype for an outside individual (II-1) is homozygous normal, III-1, III-2 and III-3 must be carriers (heterozygotes). They are not affected but could only have inherited the recessive gene from II-2. Next, II-3, II-5, and II-6 each have a $\frac{2}{3}$ chance of being a carrier and a $\frac{1}{3}$ chance of being homozygous normal. They are not affected, but they are carrier*carrier offsprings. Like I-1, II-4 and II-7 have a high probability of being homozygous normal as they are outside the family. III-4, III-5, III-6, III-7, III-8, and III-9 all have a $\frac{1}{3}$ chance of being carriers and a $\frac{2}{3}$ chance of being homozygous normal. One parent of each is probably homozygous normal, the other has a $\frac{2}{3}$ chance of being a carrier and a 1 in 2 chance of passing on the recessive allele if they were a carrier.
Example 2: Linkage mapping using pedigrees is the disease linked to the marker given the pedigree below. (Dominant inheritance)
- Two problems: (1) we don’t know the phase, even if the genes are linked, we don’t know arrangement of alleles (cis or trans) on the chromosomes in Dad: D1 d2 or D2 d1. Solution: take the average of the likelihoods of linkage: L($\theta)=\frac{1}{2}L(\theta|phase 1)+\frac {1}{2}L(\theta|phase 2)$; (2) how can we compare the probability of linkage to the probability of no linkage. Solution: take the ratio (i.e. odds) of the likelihood of linkage [L($\theta$)=L(MLE of $\theta$)] versus the likelihood of no linkage [L($\theta$)=L($\theta$=0.5)].
- Calculating LOD scores: (1) if the phase is D1 d2, then there are 4 non-recombinants and 1 recombinant, L($\theta$)=(1-$\theta)^{4}\theta$; (2) if the phase is D2 d1, then there are 4 recombinants and 1 non-recombinant, L($\theta)=\theta^{4}(1-\theta)$.
For $\theta=0.1(10cm)$, phase $1,L(\theta)=(1-0.1)^{4}*0.1=0.9^{4}*0.1$, for phase 2,$\theta =0.1:L(θ)=0.1^{4} (1-0.1)=0.1^{4}*0.9.$ At $\theta=0.5, L (\theta)=0.5^{5}$, $Z(\theta)=log_{10}\frac{{[0.9^{4}0.1+0.1^{4}0.9]}{2}}{0.5^{5}} = 0.0217.$
For other values of $\theta$, do the similar calculation: so the MLE of $\theta$, $\hat{\theta}= 0.20$.
| $\theta$ | $L(\theta$) | $L=(\theta=0.5)$ | $Z(\theta)$ |
| 0 | 0 | 0.03125 | $-\infty$ |
| 0.05 | 0.02037 | 0.03125 | -0.18586 |
| 0.10 | 0.03285 | 0.03125 | 0.02169 |
| 0.15 | 0.03937 | 0.03125 | 0.10032 |
| 0.20 | 0.0416 | 0.03125 | 0.12424 |
| 0.25 | 0.04102 | 0.03125 | 0.11815 |
| 0.30 | 0.0385 | 0.03125 | 0.09454 |
- Linkage Disequilibrium
- Linkage vs. Linkage Disequilibrium: linkage refers to the observation that two loci are inherited together (rather than be separated by recombination) in a single generation; linkage disequilibrium refers to the pattern of correlation between loci at the population level.
- Linkage and Association: linkage is the relationship between loci, and is examined within families; association is the relationship between alleles and is examined within populations.
- Linkage Disequilibrium (LD): describes the tendency of alleles to be inherited together more often than would be expected under random segregation. Extend of LD reflects the population’s history and the distance between markers. LD mapping is a promising approach for mapping genes, especially for complex-trait diseases. It is a population-based concept (not an individual or family-based concept); it has expected and observed values: looks at haplotypes instead of genotypes, observed frequencies are for haplotypes, expected haplotypes frequencies are calculated from allele frequencies.
- Forces affecting LD: (1) recombination: breaks up allelic association; (2) gene conversion: during recombination, DNA sequence information is transferred from one chromatid to another; (3) recurrent mutation: same mutation arises on different haplotype backgrounds; (4) natural selection: keeps pairs of genes/SNPs together; (5) demographic history: migration, non-random mating.
- Linkage equilibrium:$p_{ab}=p_{a} p_{b}=(1-p_{A})(1-p_{B})$ ; $p_{AB}=p_{A} p_{B}$; $p_{Ab}=p_{A} p_{b}=p_{A} (1-p_{B})$; $p_{aB}= p_{a}p_{B} = (1-p_{A})p_{B};$
- Linkage disequilibrium:$p_{ab}\not=p_{a} p_{b}=(1-p_{A})(1-p_{B})$ ; $p_{AB}=p_{A} p_{B}$; $p_{Ab}=p_{A} p_{b}=p_{A} (1-p_{B})$; $p_{aB}= p_{a}p_{B} = (1-p_{A})p_{B};$
- Measures of LD: fundamental measure: Disequilibrium coefficient (D); most commonly used measures: D’ and |D’|; $r^{2}$ or $\Delta^{2}$.
- $D_{AB}$ is the disequilibrium coefficient for locus A and locus B. D is hard to interpret.
$D_{AB}=p_{AB}-p_{A} p_{B};$ $p_{AB}=p_{A} p_{B}+D_{AB};$ $D_{aB}=p_{a} p_{B}-D_{AB};$ $D_{ab}=p_{a} p_{b}+D_{AB};$
$D'_{AB}=\begin{cases}\frac{D_{AB}}{min(p_{A} p_{B},p_{a} p_{b})},D_{AB} \\\frac{D_{AB}} {min(p_{A} p_{b},p_{a} p_{B})},D_{AB}>0,\end{cases}$ it ranges between -1 and +1, when allele frequencies are small, D' is more likely to take extreme values, D’ of -1 or +1 implies that least one potential haplotype was not observed (no evidence for recombination between markers).
$r^{2}$ or $\Delta^{2}=\frac{D_{AB}}{p_{A}(1-p_{A})p_{B}(1-p_{B})}$ it ranges between 0 and 1; $r^{2}=1$ when the markers provide identical information; $r^{2}= 0$ when the markers are in perfect equilibrium; not as strongly affected by extreme allele frequencies.
Information from measurements: when D’ is high and $r^{2}$ is high indicates the tendency toward presence of only 2 haplotypes, with similar allele frequencies of the 2 loci; when D’ is high and $r^{2}$ is low indicates the tendency toward presence of only 3 haplotypes (for example, a young SNP ancestrally), with large difference in allele frequencies of the 2 loci; when D’ is low and $r^{2}$ is low indicates the tendency toward presence of all 4 haplotypes and random coupling of alleles.
- Disequilibrium will decay each generation in a large population, after t generations: $D_{t}=(1-\theta)^{t} D_{0}$.
- Genetic Testing Issues
- Genetic Test: analysis of chromosomes, genes and/or gene products (proteins) to determine whether there is an abnormality present that is causing or will cause a genetic condition/disorder.
- Proportion of Genes Shared: first degree relatives (50%): sibs, parents, children, dizygotic twins; second degree relatives (25%): uncles, aunts, nieces, nephews, grandparents, grandchildren, half-sibs, double first cousins; third degree relatives (12.5%): first cousins, half-uncles/aunts, half-nieces/nephews.
- Genetic tests are different from other medical tests:
- Medical tests done to detect a current medical condition. It may be done on healthy individuals to determine future risk for a genetic condition (predictive tests).
- Genetic test may need to be performed on affected family member before patient can be tested.
- Genetic test results may have implications for healthcare and life decisions of other family members.
- Possible insurance implications and potential for stigmatization and discrimination.
- Genetic tests currently offered on a population level: newborn screening; multiple marker screening for pregnant women to screen for increased risk for chromosome abnormalities (e.g. Down syndrome) and neural tube defects (e.g. spina bifida); Cystoic fibrosis screening offered preconceptionally and to pregnant couples; carrier testing for Tay-Sachs disease, Sickle cell anemia; Prenatal testing offered to women 35 and older.
- Genetic testing is currently offered to individuals with symptoms consistent with a genetic condition to establish, confirm or rule out a diagnosis; family history of a genetic condition.
- Uses of Genetic Testing:
- Diagnostic Testing: used to establish or confirm a diagnosis in a patient who has symptoms suggestive of a genetic condition.
- Predictive testing: (1) presymptomatic, eventual development of symptoms is certain when the gene mutation is present; (2) predispositional (eventual development of symptoms is likely but not certain when the gene mutation is present, e.g., breast cancer.
- Carrier testing: offered to patients based on family history of a genetic condition or ethnicity.
- Prenatal testing: offered during pregnancy to assess fetal status when there is an increased risk of having a child with a genetic condition due to maternal age, family history, ethnicity, abnormal screening test or ultrasound evaluation.
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD): used with IVF and involves genetic testing on early embryos prior to implantation to rule out a genetic condition.
- Newborn screening: screen for genetic disorders which can result in severe medical problems, metal retardation or even death in newborns. Some of the conditions can benefit form early treatment.
- Pharmacogenetic testing: to identify gene changes in metabolic pathways that determine drug response, both for therapeutic effects and adverse effects. Examples may be genetic testing for CYP450.
- Prognostic testing.
- Forensic testing.
- Identity testing: who is the parent.
- Genetic Testing Challenges:
- Testing for many genetic conditions not yet standard of care. Few practice guidelines exist.
- Laboratories may offer different testing, even for the same genetic condition.
- Many genetic tests are costly, low detection rate.
- Genetic test results may be uninterpretable.
- Moving target; rapid evolution of information.
- Genetic Association Studies: an observational study that tests for a statistically significant correlation between a genetic marker (the exposure) and a phenotype (the outcome).
- Genetic markers and phenotypes
- Genetic marker = any measurable genetic, polymorphism: varies across individuals, groups, or populations can occur in coding or non-coding regions of the genome.
- Phenotype = any measurable trait: quantitative (height, blood pressure, glucose levels); qualitative (heart disease, cancer, hair color).
- Genetic association studies can be planned and analyzed using the QMSSI framework: question, measure, sampling, statistics, and inferences.
- Study question: need to identify the population of interest (age, race, gender, geographic), the phenotype being studied and whether the study will look at specific genes with biological/positional relevance or agnostically search for new genomic regions of interest.
- Measures: methods for measuring both must be characterized (Valid? Reliable?); must be described (quantitative phenotypes such as normally distributed, mean, variance and qualitative phenotypes such as blood pressure vs. hypertensive).
- Sampling: family based (twin studies, heritability studies, linkage studies) vs. population based sampling
- Statistics: statistical tests for genetic association studies largely determined by type of sampling and type of outcome.
- Inferences: association is not sufficient to prove causation. A positive statistical finding does not definitively mean the polymorphism tested is causing the outcome. A statistical association may be a result of direct causal relationship between SNP and outcome; confounding (linkage disequilibrium; population stratification); spurious association, false positive result.
- Gene-environment and Gene-gene Interactions
- Genes and Environment: almost all disease have a genetic component and an environmental component. How do these components interact? How to account for both effects?
- Model 1: Neither the genotype nor the environment along increase risk
- Model 2: The genotype exacerbates the effect of the risk factor
- Model 3: The risk factor exacerbates the effect of the genotype.
- Model 4: The genotype and the risk factor each influence risk by themselves:
- The study of gene-environment interactions, use epidemiologic techniques to identify both components (gene and environment):
- Case-control studies
- Cohort studies
- Case only studies
- Case-parental control
- Affected relative pair
- Twin studies
To model Gene-Environment interactions:$ outcome = gene + environment + gene-environment interaction. Y=G+E+GXE $
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.umich.edu
Translate this page: